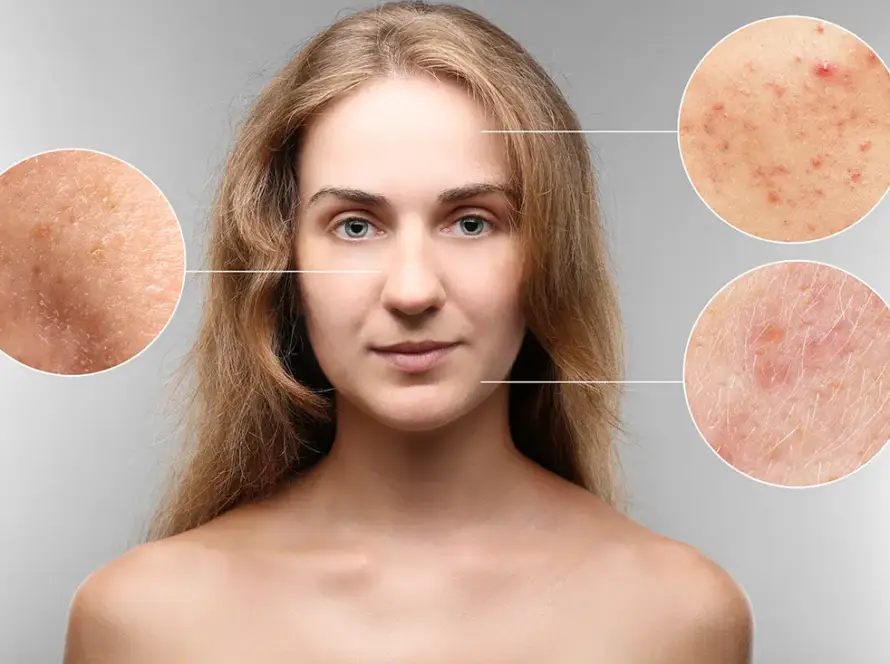
Struggling with acne? Understanding the different types of acne, causes, and effects can make a difference
Acne isn’t just a skin condition – it’s a deeply personal experience that can affect how you look and feel every day. But not all acne is the same. From small, stubborn blackheads to painful cysts, acne comes in many forms, each with its own causes, severity, and treatment needs. Understanding the type of acne you’re dealing with is the first step toward finding the right solution.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of acne – from mild to severe – and break down the most common causes of acne, including hormones, stress, and skincare habits. With this knowledge, you’ll be better prepared to understand your skin and take control of your acne journey.
How to identify the type of acne?
Understanding the different kinds of acne can help you find the best way to treat it. Acne comes in various types, each presenting with different kinds of lesions or blemishes. Acne vulgaris is the most common form of acne, affecting both teenagers and adults. Characterized by acne lesions such as comedones, inflammatory papules, and pustules, acne vulgaris can present in various forms, ranging from mild to severe acne. These can be broadly classified into two main categories: inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne. Subtypes of acne within these two categories include:
- whiteheads
- blackheads
- papules
- pustules
- nodules
- cysts
Although “breakout” is a popular way to refer to acne, it’s not fully accurate because certain types of acne don’t spread widely on the skin.
While acne is commonly linked to hormonal changes during the teenage years, adults can (and frequently do) experience it as well.
Different causes of acne
Acne is a multifactorial skin condition influenced by a variety of internal and external factors. Let’s take a look together at the differing primary causes of acne:
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones during puberty, menstruation, and other life stages are very common acne triggers.
- Excess oil production: Increased androgen levels lead to excessive sebum production or hyperseborrhoea. These overactive sebaceous glands lead to increased oil production, clogging pores and causing acne.
- Bacteria: The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) colonize hair follicles, triggering inflammation and acne lesions.
- Genetics: Acne has a strong hereditary component so a family history of acne can make individuals more prone to developing the condition. The genetic factors have a high impact on the severity and onset of this condition.
- Abnormal keratinization: The process of skin cells shedding is disrupted, leading to clogged hair follicles and the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads).
- Diet: While the role of diet is debated, some studies suggest that high glycemic foods or dairy products may exacerbate acne in some individuals.
- Stress: Stress hormones can trigger or worsen acne by influencing hormone levels and immune responses.
- Skin care products: Oily or comedogenic (pore-clogging) products can clog pores and contribute to acne.
Now that you understand the root causes of acne, explore how our cutting-edge treatments target these issues at their source. Learn more about acne treatments at Blemish Clinic and book your appointment here.
Different types of acne
Non-inflammatory or mild acne
These are typically mild forms of acne that usually don’t cause redness or swelling and include clogged pores that aren’t infected. Let’s take a closer look at the two main types.
Whiteheads (closed comedones)
These occur when a hair follicle is clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria but remains closed, causing a small, whitish bump on the skin.
Blackheads (open comedones)
In this mild acne type, the clogged follicle remains open, and the trapped material oxidizes upon exposure to air, turning it black.
Inflammatory acne (moderate or severe)
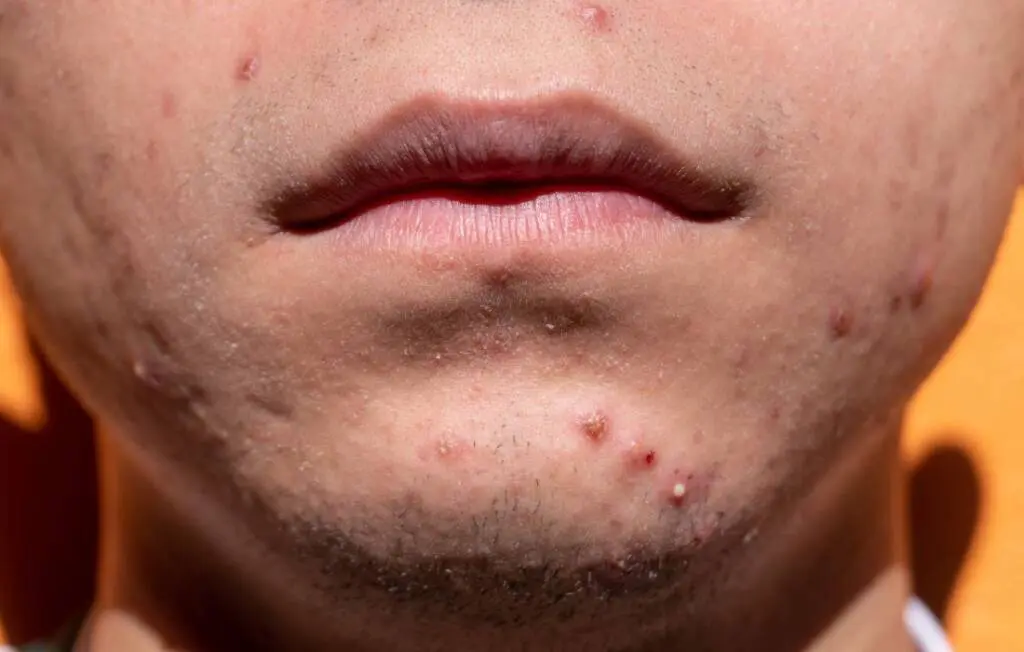
Inflammatory acne are characterised by swelling, redness, and discomfort. They are more severe, often painful lesions due to inflammation in the pores and are typically triggered by excess sebum. When mixed with dead skin cells, they clog the pores. They are typically more severe than non-inflammatory types. They include the following:
Papules
Small, raised, red bumps caused by infected or irritated pores. They are tender to the touch and do not have pus.
Pustules
These are similar to papules but filled with pus. They appear as red, inflamed bumps with a white or yellow centre.
Nodules
These are large, painful lumps deep within the skin, formed when the build-up inside a clogged pore spreads deeper. Nodules are more severe and often do not form a head.
Cysts (cystic acne)
Cysts are the most severe form of acne. They are large, pus-filled, painful bumps that can cause scarring. Cystic acne forms deep within the skin and are often resistant to topical treatments. Thus, it typically requires prescription medications, such as isotretinoin, and often benefits from professional medical treatments. Cystic acne are also the type of acne more common in teens or people with oily skin.
Acne conglobata
This is a severe form of cystic acne that involves interconnected nodules and cysts, often resulting in deep scars. It’s usually found on the chest, back, arms, and face and primarily affects men.
Acne mechanica
This type of acne is caused by some kind of skin irritation, friction, pressure, or heat, commonly occurring in athletes or individuals who wear tight clothing or carry backpacks. It results in small papules or pustules in areas subject to pressure.
Acne fulminans
This is a rare, aggressive form of inflammatory acne that comes with systemic symptoms like fever and joint pain. It is more commonly seen in males and may require systemic treatment with steroids or other medications.
Acne rosacea
While often confused with traditional acne, rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes redness, visible blood vessels, and pimples on the face. Unlike acne vulgaris, rosacea does not feature comedones (blackheads or whiteheads).
Once you’ve identified your acne type, check out our acne treatment options designed for mild, moderate, and severe acne.
Management and acne treatment options
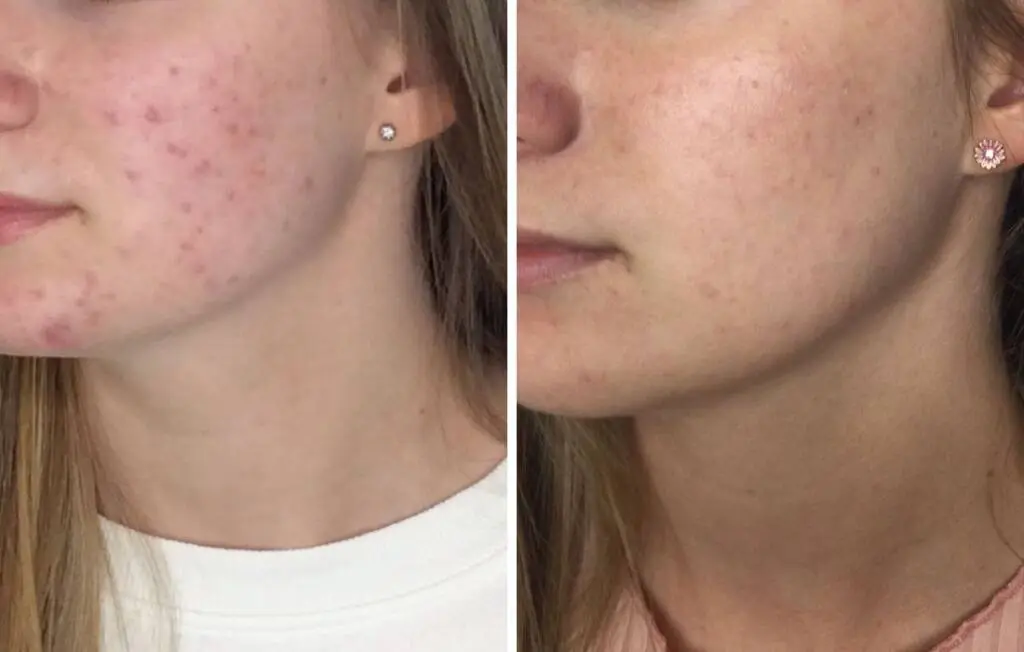
It’s possible to have multiple types of acne at once, each requiring different management approaches depending on its severity. Treating acne may include:
Topical treatments
Topical treatments may help reduce clogged pores and bacteria in particular over-the-counter or prescription products containing:
- Benzoyl peroxide – primarily used in treating mild to moderate acne, targets bacteria, reducing acne lesions.
- Salicylic acid – also mainly used in treating mild to moderate acne, especially effective for unclogging hair follicles.
- Retinoids – For those with mild inflammatory acne they help prevent clogged pores and are often recommended as a first-line treatment in dermatology.
Oral medications
The following medications may be prescribed for moderate to severe acne:
- Antibiotics – may be combined with topical treatments to reduce bacterial load and inflammation and are often prescribed for short-term use.
- Hormonal treatments (like birth control pills) – particularly beneficial for women with adult acne, hormonal treatments can regulate oil production.
- Isotretinoin – prescribed for cystic or severe acne, offering long-term remission in many cases but only under careful medical supervision due to its potential side effects, including depression.
Professional procedures
The following procedures can help with more severe acne or resistant forms of acne:
- Chemical peels – Also called skin peels, help remove the top layers of your skin enabling new skin layers to grow that usually look smoother, healthier and less scared than the old skin. When treating inflammatory acne, peels based on salycylic acid are the most commonly suggested treatment.
- Laser therapy – different laser and light therapies treat different kinds of acne and the results vary. This is why most often, several treatments are necessary to deliver visible results.
- Drainage procedures – involve creating a small opening in the blemish with a needle or surgical blade. The dermatologist can then drain and remove what is inside.
View more information about the Acne Treatments that we offer.
GlycoAla PDT
- A novel and effective modality in treating all kinds of acne. This safe, effective treatment is designed for skin rejuvenation and conditioning, oily skin, skin purification and enhancement. GlycoAla PDT therapy boosts skin health and targets overactive sebaceous glands, resulting in a noticeable reduction in oil levels. This treatment is specific to Blemish Clinic!
Preventing Acne
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, avoiding oily products, and managing stress levels can help reduce the likelihood of breakouts. Use non-comedogenic products to prevent pore blockages, remove dead skin cells and make sure to cleanse your skin gently. Some of the most common and effective preventive tips include the following:
- Washing your face gently twice a day to remove excess oil and bacteria
- Using oil-free, non-comedogenic products to avoid clogging pores
- Exfoliating by gently scrubbing your face to remove dead skin cells and excess sebum
- Not picking at pimples, as this can worsen inflammation and lead to acne scars
- Staying hydrated and eating a balanced diet, which may help minimize acne flare-ups in some individuals
Psychological impacts of acne
Research shows that nearly 85% of teenagers experience acne, with emotional distress reported in 50% of those affected. This is commonly the case in adolescence when peer relationships are highly valued so the visible nature of acne can lead to social anxiety, lower self-esteem and higher vulnerability to psychological issues such as depression. Although commonly associated with younger adults, acne significantly affect adults as well. Teenagers often experience acne due to surging hormones, leading to oil production and clogged pores. Adults, on the other hand, may struggle with hormonal acne around the jawline, often linked to stress, diet, or hormonal changes like pregnancy or menopause.
Why Understanding Acne Types and Causes Matters
Acne is more than a skin condition – it can deeply affect confidence and emotional well-being, from the self-consciousness of teenage years to the stress and anxiety often experienced by adults. Understanding the type of acne you have and its causes is the first and most important step toward effective treatment. By identifying your specific acne type and addressing the underlying causes, you can prevent complications like scarring and manage inflammation early. For persistent or severe acne, consulting a dermatologist is essential to creating a personalized treatment plan. At Blemish Clinic, we offer innovative solutions, including GlycoAla PDT, tailored to your unique skin needs. Take the first step toward healthier skin and greater confidence by scheduling a consultation with our specialists today.